| 86-13906852089 | Follow Us |  |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
Compression spring parameters
DATE:2022.06.17 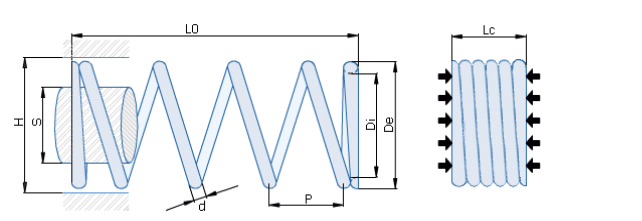 Physical parameters ◼ d (wire diameter): This parameter describes the diameter of wire used as material for spring. ◼ S (shaft): This parameter describes the maximum diameter of spring shaft in industrial applications. Tolerance for this parameter is (+-)2%(indicative). ◼ Di (internal diameter): Internal diameter of a spring can be calculated by subtracting the doubled wire diameter from the external diameter of a spring. Tolerance for this parameter is (+-)2%(indicative). ◼ De (external diameter): External diameter of a spring can be calculated by adding the doubled wire diameter to the internal diameter of a spring. Tolerance for this parameter is (+-)2%(indicative). ◼ H (hole): This is the minimum diameter of the hole in which spring can work. Tolerance for this parameter is (+-)2%(indicative). ◼ P (pitch): Average distance between two subsequent active coils of a spring. ◼ Lc (block length): Maximal length of a spring after total blocking. This parameter is shown in the picture on right. Tolerance for this parameter is (+-)15%(indicative). ◼ L0 (free length): Free length of compression springs is measured in its uncompressed state after previous one time blocking. Tolerance for this parameter is (+-)2%(indicative). ◼ Nr of coils: This is a total number of coils in a spring - in the picture above it is equal to six. To calculate number of active coils substract two terminating coils from total number of coils. ◼ Grinding: Defines whether or not the ends of a spring are ground. |
| |||||||||||||||||||
|
©2020-2022 Shaoxing Sanyang spring Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Zhe ICP14024509-1 Technical Support:Tsheng
|